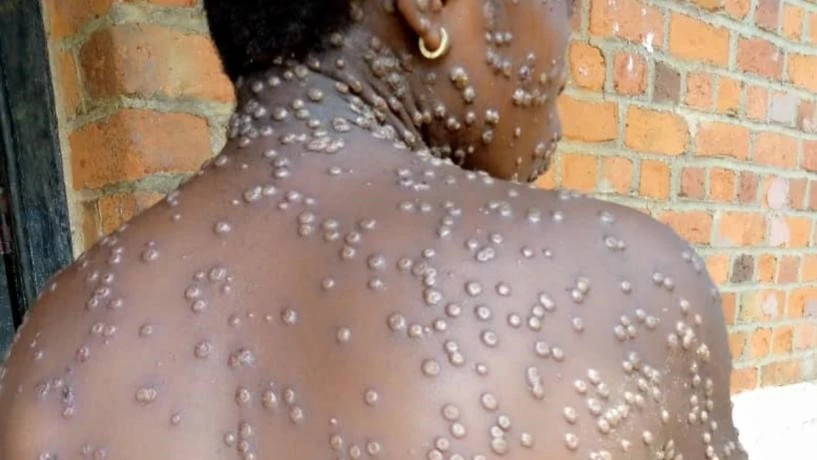
Mpox also known as monkeypox is a re-emerging viral disease that has made its presence known in parts of Africa, including Ghana. Although the number of confirmed cases in Ghana remains low, the virus’s ability to spread through close contact makes it a public health concern. It’s important to take deliberate steps to protect yourself from contacting Mpox, especially as surveillance continues to detect isolated cases across the country.
Read Also: Ghana Confirms Two Cases of Mpox in Accra: What You Need to Know
What is Mpox?

Mpox is a zoonotic disease caused by the monkeypox virus, which is closely related to the virus that causes smallpox. It is less deadly than smallpox but can still cause serious illness. Mpox is transmitted from animals to humans and from person to person through direct contact with bodily fluids, lesions, or respiratory droplets.
Symptoms of Mpox include:
- Fever
- Rash (that progresses through various stages)
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Chills and fatigue
The illness usually lasts between 2 to 4 weeks.

Mpox Mortality Rate
Mpox has two main strains: the Central African (Congo Basin) clade and the West African clade. The strain most commonly seen in West Africa, including Ghana, typically has a lower fatality rate — around 1% to 3%. However, the Congo Basin strain can have a mortality rate as high as 10%, particularly in children and immunocompromised individuals.
Although no deaths have been reported in Ghana in recent cases, the global re-emergence of Mpox underscores the importance of awareness and preventive action.
Current Situation in Ghana
As of October 2024, Ghana reported two confirmed Mpox cases — a 15-year-old male from the Western North Region and his mother. Both were treated and recovered fully. Health authorities identified and are monitoring over 30 close contacts. The Ghana Health Service (GHS) has since heightened disease surveillance, particularly at border points and international airports.
Read Also: Ministry of Health Launches Enhanced Mobile App for Health Training Admission Forms
How to Protect Yourself from Contacting Mpox

To protect yourself from contacting Mpox, here are proven strategies:
1. Limit Close Contact with Infected Individuals
Mpox spreads through direct physical contact. Avoid touching skin rashes, lesions, or bodily fluids of individuals showing symptoms. Do not share personal items such as clothing, towels, or bedding with anyone suspected of having Mpox.
2. Practice Proper Hand Hygiene
Wash your hands regularly with soap and water or use alcohol-based sanitizers, especially after being in public places or after contact with possibly contaminated surfaces.
3. Avoid Wild Animals and Undercooked Meat
Mpox can also be contracted from animals, particularly wild rodents and primates. Avoid hunting, handling, or eating bushmeat. Ensure all meat products are properly cooked.
4. Disinfect Surfaces and Wear Protection
If you live with or are caring for someone with Mpox, disinfect commonly touched surfaces and wear protective equipment like gloves and masks. Healthcare workers should use full PPE when attending to suspected cases.
5. Stay Informed and Seek Early Medical Attention
Public health authorities continue to monitor and respond to Mpox outbreaks. Stay up to date through official sources like the Ghana Health Service or WHO. If you notice symptoms, especially after exposure, report to a health facility immediately.
Ghana may have only a few confirmed cases, but that doesn’t mean we should let our guard down. With a potential mortality rate of up to 3% for the West African strain, prevention remains better than cure. Staying informed, maintaining hygiene, and avoiding high-risk contact are your best defenses.
By following these guidelines, you’re not only protecting yourself but also helping curb the spread of the virus in your community. Let’s all do our part to protect yourself from contacting Mpox and keep Ghana safe.