Hand sanitizers and brain development: When the COVID-19 pandemic broke out and spread across borders, Items like nose masks and hand sanitizers became tools to prevent or minimize the spread.
To date, they have become a part of our lives, replacing traditional hand-washing.
A new study conducted by molecular biologist Erin Cohn and his colleagues suggests that certain common household items can cause damage to supporting cells present in the brain.
These compounds are found in items like furniture, textiles, disinfectants, and glues.
Also Read: Increased Risk of Cancer Amongst Younger People
This new study was carried out based on human cell cultures and mice. The effect of such chemicals was found to be more prevalent in the early stages of brain development.
Erin Cohn tested the effect of 1,823 compounds on a group of cells known as oligodendrocytes under laboratory conditions.
He found out that these compounds either killed oligodendrocytes or stopped their maturation.
The team’s observation confirmed a link between Hand sanitizers and brain development.
What are oligodendrocytes?
Oligodendrocytes are critical components for the central nervous system (CNS) functioning.
Oligodendrocytes generate and maintain myelin, increasing the speed and efficiency of axonal signal conduction and contributing to the structure and maintenance of the ensheathed axons.
Simply put they ensure that your brain signals move at the required speed.
How do These Chemicals Find their way into The Brain?
They enter the brain when you inhale or unknowingly ingest them.
The team found some of these “brain-killing” compounds used in sanitizers, hand wipes, disinfectant sprays, and household products,
Another class of toxic compounds found in basic household items was organophosphates.
They are compounds usually found in textiles, electronics, and furniture. They act as flame retardants.
Fat-soluble organophosphates can permeate through the skin and find their way into the brain.
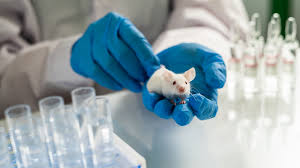
Experiment Carried Out on Mice
The researchers gave lab mice an oral dose of three quaternary compounds and found out days later that detectable levels of these compounds were inside the brain tissue of the mice.
The number of oligodendrocytes in the brain tissues of the mice had reduced after administring 10 daily doses of cetylpyridinium chloride.
cetylpyridinium chloride is also a type of quaternary compound.
“We found that oligodendrocytes – but not other brain cells – are surprisingly vulnerable to quaternary ammonium compounds and organophosphate flame retardants,” said Cohn.
You can find the Publication In the journal Nature Neuroscience.